|
|

|
Two
methods of limb bud culture exist. Chorioallantioc membrane
(CAM) grafting is a culture method commonly used in the
past. In this type of experiment, the severed limb bud is
grafted into a host egg on a Y- shaped junction of blood
vessels. The limb grows on nutrients supplied by the host
egg. A more recent application of limb bud uses no host but
a growth medium in vitro. The culture medium contains
elements essential for continued growth and antibiotics to
protect against infection. Although CAM grafts have been
used in the past, an obvious advantage of an in vitro
method is that manipulative agents, such as growth
factors and hormones, can be added to the culture
medium.
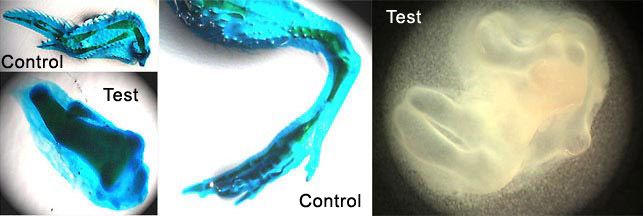
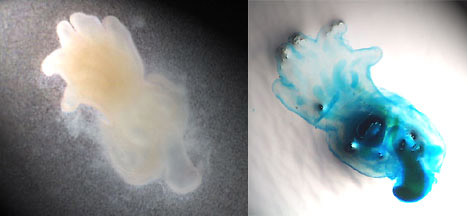
The primary purpose of this
experiment is to observe limb development by studying the
presence of cartilage in cultured limbs. The secondary
purpose is to investigate whether or not in
vitroculture can support
limb development. The control will be limbs that develop
in ovo.
Major Observations
Limbs
developed in vitroand
cartilage was observed using Alcian green staining. In some
cases, development had progressed to the point at which
cartilage began changing into bone, and, thus, was not seen
in the staining. Compared to control limbs, limbs grown in
media were not as large or organized as well.
|
|