In this section, I'll discuss limits and derivatives of trig
functions. I'll look at an important limit rule first, because I'll
use it in computing the derivative of ![]() .
.
If you graph ![]() and
and ![]() , you see that the graphs become almost
indistinguishable near
, you see that the graphs become almost
indistinguishable near ![]() :
:
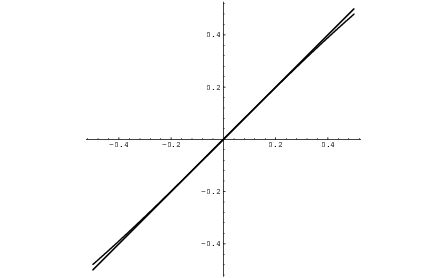
That is, as ![]() ,
, ![]() . This
approximation is often used in applications --- e.g. analyzing the
motion of a simple pendulum for small displacements. I'll use it to
derive the formulas for differentiating trig functions.
. This
approximation is often used in applications --- e.g. analyzing the
motion of a simple pendulum for small displacements. I'll use it to
derive the formulas for differentiating trig functions.
In terms of limits, this approximation says
![]()
(Notice that plugging in ![]() gives
gives ![]() .) A derivation requires the Squeeze Theorem and a
little geometry. What I'll give is not really a proof from first
principles; you can think of it as an argument which makes the result
plausible.
.) A derivation requires the Squeeze Theorem and a
little geometry. What I'll give is not really a proof from first
principles; you can think of it as an argument which makes the result
plausible.
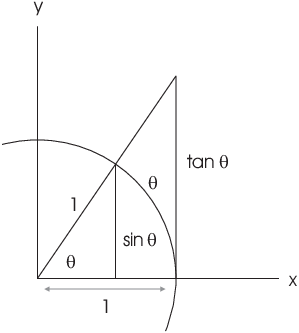
I've drawn a sector subtending an angle ![]() inside a circle of radius 1. (I'm using
inside a circle of radius 1. (I'm using ![]() instead of x, since
instead of x, since ![]() is more often used
for the central angle.) The inner right triangle has altitude
is more often used
for the central angle.) The inner right triangle has altitude ![]() , while the outer right triangle has altitude
, while the outer right triangle has altitude ![]() . The length of an arc of radius 1 and angle
. The length of an arc of radius 1 and angle ![]() is just
is just ![]() .
.
(I've drawn the picture as if ![]() is nonnegative. A
similar argument may be given if
is nonnegative. A
similar argument may be given if ![]() .)
.)
Clearly,
![]()
Divide through by ![]() :
:
![]()
As ![]() ,
, ![]() --- just plug in. By the Squeeze Theorem,
--- just plug in. By the Squeeze Theorem,
![]()
Taking reciprocals, I get
![]()
Example. Compute ![]() .
.
Plugging in ![]() gives
gives ![]() . I have to
do some more work.
. I have to
do some more work.
\def\square{\vbox{\hrule\hbox{\vrule height1.5ex\hskip1.5ex\vrule}\hrule}}
The limit formula has the form
![]()
In this example, ![]() . In order to apply the
formula, I need
. In order to apply the
formula, I need ![]() on the bottom of the fraction
as well as inside the sine: They must "match". I can't do
much about the
on the bottom of the fraction
as well as inside the sine: They must "match". I can't do
much about the ![]() inside the sine, but I can make a
inside the sine, but I can make a ![]() on the bottom easily using algebra:
on the bottom easily using algebra:
![]()
Let ![]() . As
. As ![]() ,
, ![]() . So
. So
![]()
I'll often omit writing a substitution like ![]() . Once I see that I have something of the form
. Once I see that I have something of the form ![]() where
where ![]() , I know it has limit 1.
, I know it has limit 1.![]()
Example. Compute ![]() .
.
Plugging in gives ![]() .
.
The idea here is to create terms of the form ![]() , to which I can apply my limit
rule. I'll describe the steps I'll take first, then do the
computation.
, to which I can apply my limit
rule. I'll describe the steps I'll take first, then do the
computation.
(a) I'll convert the tangent term to sine and cosine. This is because
my fundamental rule involves sine, and I also know that ![]() as
as ![]() (so cosine terms
aren't much of an issue).
(so cosine terms
aren't much of an issue).
(b) I'll divide all the terms on the top and the bottom by x. This is
in preparation for making terms of the form ![]() .
.
(c) I'll use the trick I used earlier to fix up numbers so the sine
terms all have the form ![]() , where the thing inside the sine and the thing on
the bottom match.
, where the thing inside the sine and the thing on
the bottom match.
Here's the computation:
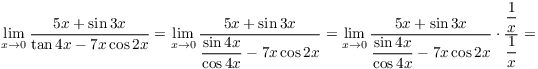
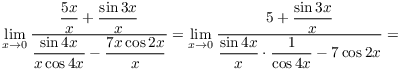
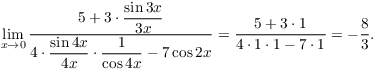
As ![]() , the terms
, the terms ![]() and
and ![]() both
go to 1 by the sine limit formula. On the other hand, the terms
both
go to 1 by the sine limit formula. On the other hand, the terms ![]() and
and ![]() both go to 1, since
both go to 1, since ![]() and
and ![]() is continuous.
is continuous.![]()
Example. (a) Compute ![]() .
.
(b) Compute ![]() .
.
(a) Plugging in gives ![]() . The limit
may or may not exist.
. The limit
may or may not exist.
The idea is to use a trig identity ![]() to change the cosines into sines, so I can use my
sine limit formula. It is kind of like multiplying the top and bottom
of a fraction by the conjugate to simplify a radical expression.
to change the cosines into sines, so I can use my
sine limit formula. It is kind of like multiplying the top and bottom
of a fraction by the conjugate to simplify a radical expression.
![]()
![]()
(b) If you draw the graph near ![]() with a graphing
calculator or a computer, you are likely to get unusual results.
Here's the picture:
with a graphing
calculator or a computer, you are likely to get unusual results.
Here's the picture:
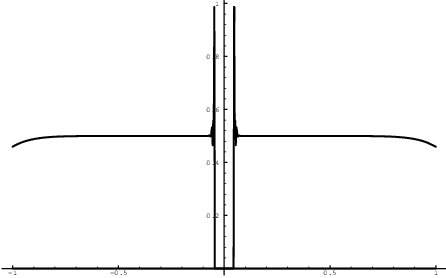
The problem is that when x is close to 0, both ![]() and
and ![]() are very close to 0 ---
producing overflow and underflow.
are very close to 0 ---
producing overflow and underflow.
Actually, the limit is easy: Let ![]() . When
. When ![]() ,
, ![]() , so
, so
![]()
For the last step, I used the result from the previous problem.![]()
Example. Compute ![]() .
.
If you set ![]() , you get
, you get ![]() . Sigh.
. Sigh.
I'll see what I can tell from the graph:
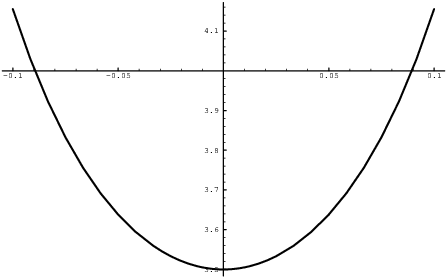
It looks as thought the limit is defined, and the picture suggests that it's around 3.5.
First, I'll break the tangents down into sines and cosines:
![]()
Next, I'll force the ![]() form to appear. Since I've got
form to appear. Since I've got ![]() and
and ![]() , I need to make a
, I need to make a ![]() and a
and a ![]() to match:
to match:
![]()
Now take the limit of each piece:
![]()
The limit of a product is the product of the limits:
![]()
Derivatives of trig functions.
I'll begin with a lemma I'll need to derive the derivative formulas.
Lemma. ![]() .
.
Proof.
![]()
![]()
Proposition.
(a) ![]() .
.
(b) ![]() .
.
(c) ![]() .
.
(d) ![]() .
.
(e) ![]() .
.
(f) ![]() .
.
Proof. To prove (a), I'll use the sine limit formula
![]()
I'll also need the angle addition formula for sine:
![]()
Let ![]() . Then
. Then
![]()
![]()
The first term goes to 0 by the preceding lemma. Hence,
![]()
That is,
![]()
To derive the formula for cosine, I'll use the angle addition formula for cosine:
![]()
Let ![]() . Then
. Then
![]()
![]()
![]()
I won't do the proofs for the remaining trig functions. The idea is to write
![]()
Then you can use the derivative formulas for sine and cosine together with the quotient rule or the chain rule to compute the derivatives.
As an example, I'll derive the formula for cosecant:
![]()
Example. Compute the following derivatives.
(a) ![]() .
.
(b) ![]() .
.
(c) ![]() .
.
(d) ![]() .
.
(e) ![]() .
.
(a)
![]()
(b)
![]()
(c)
![]()
(d)
![]()
(e)
![]()
Example. For what values of x does ![]() have a horizontal tangent?
have a horizontal tangent?
![]()
So ![]() where
where ![]() . In the range
. In the range
![]() , this happens at
, this happens at ![]() . So
. So ![]() for
for ![]() , where n is any integer.
, where n is any integer.![]()
Copyright 2018 by Bruce Ikenaga