The Fibonacci numbers are defined by the following recursive formula:
![]()
![]()
Thus, each number in the sequence (after the first two) is the sum of the previous two numbers.
(Some people start numbering the terms at 1, so ![]() ,
, ![]() , and so on. But the recursion is
the same.)
, and so on. But the recursion is
the same.)
The first few Fibonacci numbers are:
![]()
Fibonacci numbers have been extensively studied. Koshy [1] and Rao [2] have extensive lists of Fibonacci identities; Koshy also has many applications. The Fibonacci Quarterly is a journal devoted to Fibonacci numbers and related topics.
Example. Express each of the following as a single Fibonacci number.
(a) ![]() .
.
(b) ![]() .
.
(c) ![]() .
.
(a) The number after ![]() and
and ![]() is
is ![]() , so
, so
![]()
(b) Since ![]() ,
,
![]()
(c)
![]()
Example. Prove that if ![]() , then
, then
![]()
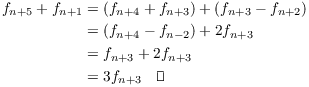
Many results about Fibonacci numbers can be proved by induction.
Example. Prove that
![]()
For ![]() , the left side is
, the left side is ![]() and the right side is
and the right side is
![]()
The result is true for ![]() .
.
Suppose the result holds for n:
![]()
I'll prove it for ![]() .
.
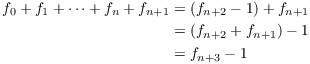
This proves the result for ![]() , so the result is true for
all
, so the result is true for
all ![]() by induction.
by induction.![]()
Example. Prove that for ![]() ,
,
![]()
For ![]() , the left side is
, the left side is
![]()
The right side is
![]()
The result is true for ![]() .
.
Assume the result for n:
![]()
Prove the result for ![]() :
:
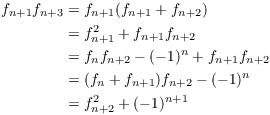
This proves the result for ![]() , so it's true for
, so it's true for ![]() by induction.
by induction.![]()
Example. ( An explicit formula for the Fibonacci numbers)
(a) Let
![]()
Prove:
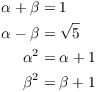
(b) Prove that
![]()
(a)
![]()
![]()
For the third and fourth equations, note that ![]() and
and ![]() are roots of the quadratic
equation
are roots of the quadratic
equation
![]()
So:
![]()
![]()
(b) For ![]() , I have
, I have ![]() . The right side
of the equation above becomes
. The right side
of the equation above becomes
![]()
The result is true for ![]() .
.
For ![]() , I have
, I have ![]() . The right side
of the equation above becomes
. The right side
of the equation above becomes
![]()
![]()
The result is true for ![]() .
.
Assume that the result is true for all ![]() . In particular,
. In particular,
![]()
![]()
I'll prove the result for ![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
![]()
This proves the result for ![]() , so the result is true for
all
, so the result is true for
all ![]() by induction.
by induction.![]()
[1] Thomas Koshy, Fibonacci and Lucas Numbers with Applications. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2001.
[2] K. Subba Rao, Some properties of Fibonacci numbers, American Mathematical Monthly, (10) 60 (1953), 680--684.
Copyright 2019 by Bruce Ikenaga