A function ![]() is a function of several variables if
is a function of several variables if ![]() --- that is, if there is more than one
input variable.
--- that is, if there is more than one
input variable.
For example a function ![]() is
a parametrized surface in
is
a parametrized surface in ![]() . Here's a picture of
. Here's a picture of
![]()
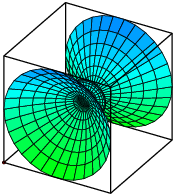
Or consider a function ![]() . Its
graph is a surface in
. Its
graph is a surface in ![]() . Here's a picture of the graph of
. Here's a picture of the graph of ![]() :
:
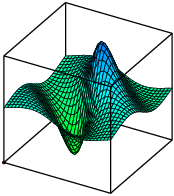
Functions of several variables occur in many real world situations
--- in fact, most measurable quantities depend on many factors or
variables. For example, the temperature at a point in space may be a
function of its coordinates ![]() . The ideal gas law
. The ideal gas law ![]() relates the pressure p, the volume
V, and the temperature T of an ideal gas. I can regard any one of
these three variables as a function of the other two; for example,
writing
relates the pressure p, the volume
V, and the temperature T of an ideal gas. I can regard any one of
these three variables as a function of the other two; for example,
writing ![]() views p as a
function of V and T.
views p as a
function of V and T.
Example. A function ![]() is defined by
is defined by
![]()
Evaluate ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
You substitute values into a function of several variables in the
obvious way. For instance, to evaluate ![]() , I set
, I set ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() in the formula for f:
in the formula for f:
![]()
Likewise,
![]()
Definition. For a function ![]() :
:
(a) The domain is the set of all points in
![]() where f is defined.
where f is defined.
(b) The image (or the
range) is the set of all outputs of f in ![]() .
.
Remark. I'm following the usual convention:
For functions ![]() to
refer to the set of points in
to
refer to the set of points in ![]() where the function is defined as the domain of the function. Thus, for the function
where the function is defined as the domain of the function. Thus, for the function
![]() , the
"domain" is the set of points
, the
"domain" is the set of points ![]() such that
such that ![]() , i.e.
, i.e. ![]() .
.
In more advanced courses, a more precise definition of a function requires that the "domain" be included as part of the function's definition. In that context, what we're calling the "domain" is referred to as the natural domain (the "biggest possible set" where the function is defined).
Example. A function of 2 variables is defined by
![]()
Describe the set of points ![]() for which f is undefined. What is the domain of f?
for which f is undefined. What is the domain of f?
![]() is undefined when the denominator is 0:
is undefined when the denominator is 0:
![]()
Thus, f is undefined for points ![]() on either of the lines
on either of the lines ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
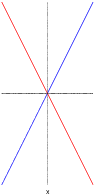
The domain is the set of points ![]() which are not on
which are not on ![]() or
or ![]() -- i.e. the points such that
-- i.e. the points such that ![]() .
.![]()
Example. A function of 2 variables is defined by
![]()
Describe the set of points ![]() for which f is undefined. What is the domain of f?
for which f is undefined. What is the domain of f?
The natural log function is undefined for inputs which are less than
or equal to 0. So ![]() will be undefined if
will be undefined if
![]()
That is, f is undefined at points ![]() where
where ![]() . They are the points lying on or above the
line
. They are the points lying on or above the
line ![]() :
:
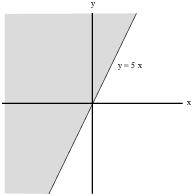
The domain is the set of points ![]() below the line
below the line ![]() .
.![]()
Example. A function of 2 variables is defined by
![]()
Describe the set of points ![]() for which f is undefined. What is the domain of f?
for which f is undefined. What is the domain of f?
Since the square root of a negative number is undefined, ![]() is undefined for
is undefined for
![]()
That is, f is undefined at points ![]() lying outside the unit circle
lying outside the unit circle ![]() .
.
The domain is the set of points ![]() on or inside the unit circle
on or inside the unit circle ![]() .
.![]()
Example. Describe the image (or the range) of
the function ![]() .
.
The image of a function is the set of outputs. What are the outputs
of the inverse tangent function ![]() ?
?
For any x and y,
![]()
I know that ![]() attains every
value between
attains every
value between ![]() and
and ![]() , and if I set
, and if I set ![]() I have
I have ![]() .
.
Therefore, the image of f is ![]() .
.![]()
A function of several variables can be pictured in many ways. For
example, you can draw the graph of a function
of 2 variables ![]() . Because
plotting points in 3 dimensions is tedious and difficult, you'd
probably use software to draw the graph.
. Because
plotting points in 3 dimensions is tedious and difficult, you'd
probably use software to draw the graph.
for functions ![]() , you
may also get a "picture" of the function by drawing its level sets. A level set for f is obtained by
setting
, you
may also get a "picture" of the function by drawing its level sets. A level set for f is obtained by
setting ![]() , where c is a constant. By using
different values for c, you get a picture of the "levels"
of the function.
, where c is a constant. By using
different values for c, you get a picture of the "levels"
of the function.
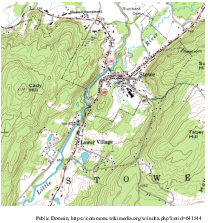
You may have seen topographic maps, where the level curves are referred to as contour lines. They represent lines along which the altitude ("z") is constant:
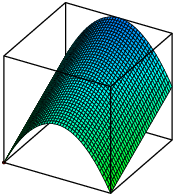
Example. Sketch the graph of ![]() , and some of the contour lines.
, and some of the contour lines.
Here's the graph of the function, produced by a computer:
I can use a computer to sketch the level curves, but this example is simple enough that I'll analyze it first. I get level curves by setting z to specific numbers and graphing the curves I get.
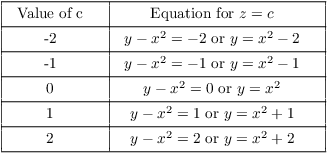
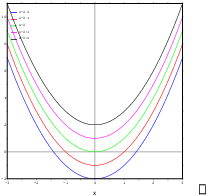
You can see the level curves are a family of parabolas.
For a function of 3 variables ![]() , setting
, setting ![]() for various numbers c produces level surfaces. If you interpret
for various numbers c produces level surfaces. If you interpret ![]() as the temperature at a point
as the temperature at a point ![]() in space, then a level surface
in space, then a level surface ![]() is the set of points in space where the
temperature is c.
is the set of points in space where the
temperature is c.
Example. Describe some level surfaces for the
function ![]() .
.
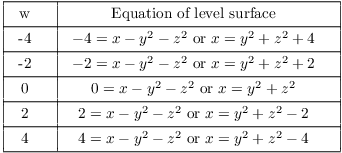
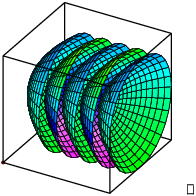
The level surfaces are paraboloids opening along the x-axis.
Copyright 2018 by Bruce Ikenaga